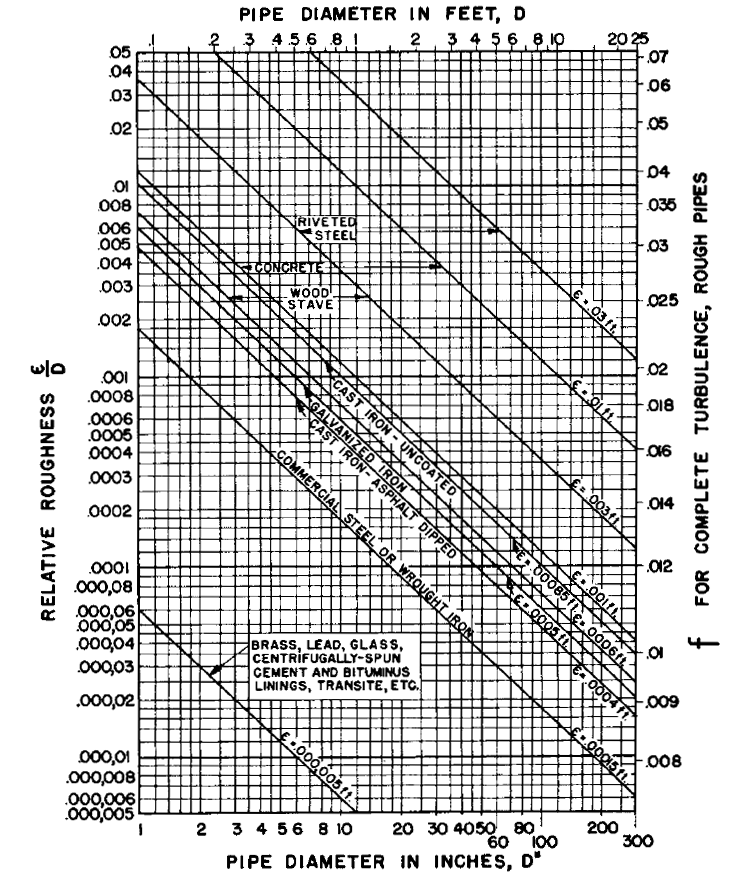
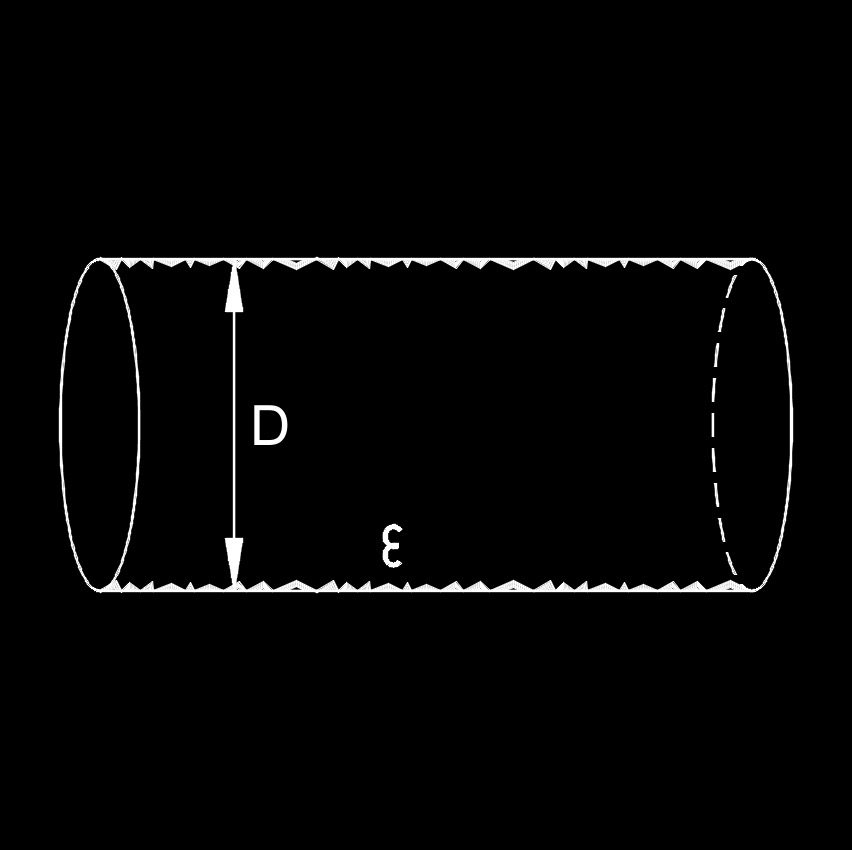
Relative Roughness. Relative roughness - ratio absolute roughness pipe duct diameter - important calculating pressure loss ducts pipes the Colebrook Equation . Relative roughness be expressed as. = / h (1) . = relative roughness . = roughness of duct, pipe tube surface (m, ft)
 Note: Pipes have absolute roughness equal or than 0.000005 feet considered exhibit "smooth pipe" characteristics. Relative roughness friction factors new, clean pipes flow 60°F (15.6°C) water (Hydraulic Institute Engineering Data Book, Reference 5) (1 meter 39.37 = 3.28 ft).
Note: Pipes have absolute roughness equal or than 0.000005 feet considered exhibit "smooth pipe" characteristics. Relative roughness friction factors new, clean pipes flow 60°F (15.6°C) water (Hydraulic Institute Engineering Data Book, Reference 5) (1 meter 39.37 = 3.28 ft).
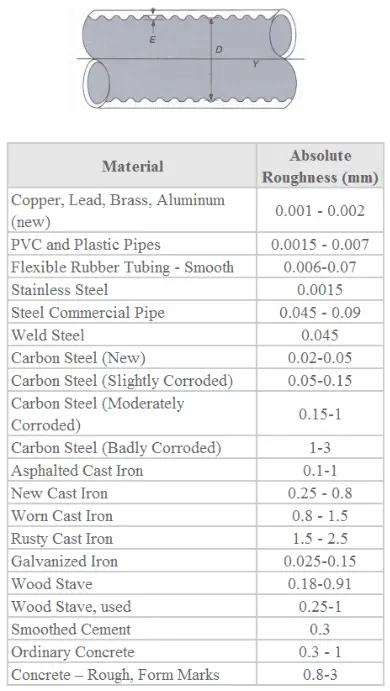
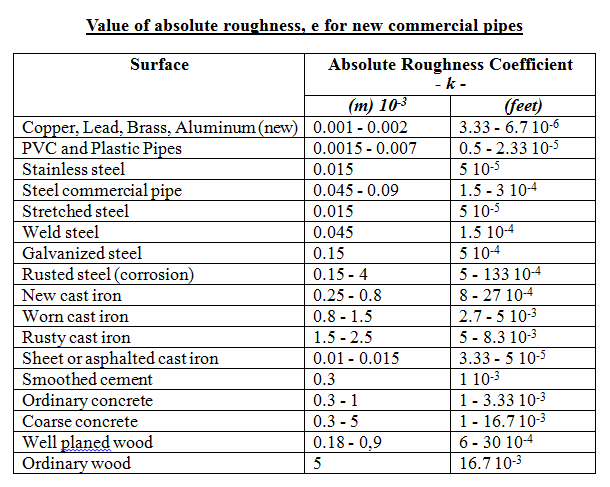
 The roughness value, denoted e, used the calculating relative roughness of pipe the size its diameter. Absolute Roughness. roughness of pipe normally in mm inches common values range 0.0015 mm PVC pipes to 3.0 mm rough concrete pipes.
The roughness value, denoted e, used the calculating relative roughness of pipe the size its diameter. Absolute Roughness. roughness of pipe normally in mm inches common values range 0.0015 mm PVC pipes to 3.0 mm rough concrete pipes.
 9.4 Chapter 9 5 pipe wall thickness, in. 5 flow velocity, ft/s 5 equivalent roughness, in. ft (to match units pipe diameter) 5 kinematic viscosity a fluid, ft2/s DX 5 horizontal pipe deflection, in. DY 5 vertical pipe deflection, in.
9.4 Chapter 9 5 pipe wall thickness, in. 5 flow velocity, ft/s 5 equivalent roughness, in. ft (to match units pipe diameter) 5 kinematic viscosity a fluid, ft2/s DX 5 horizontal pipe deflection, in. DY 5 vertical pipe deflection, in.
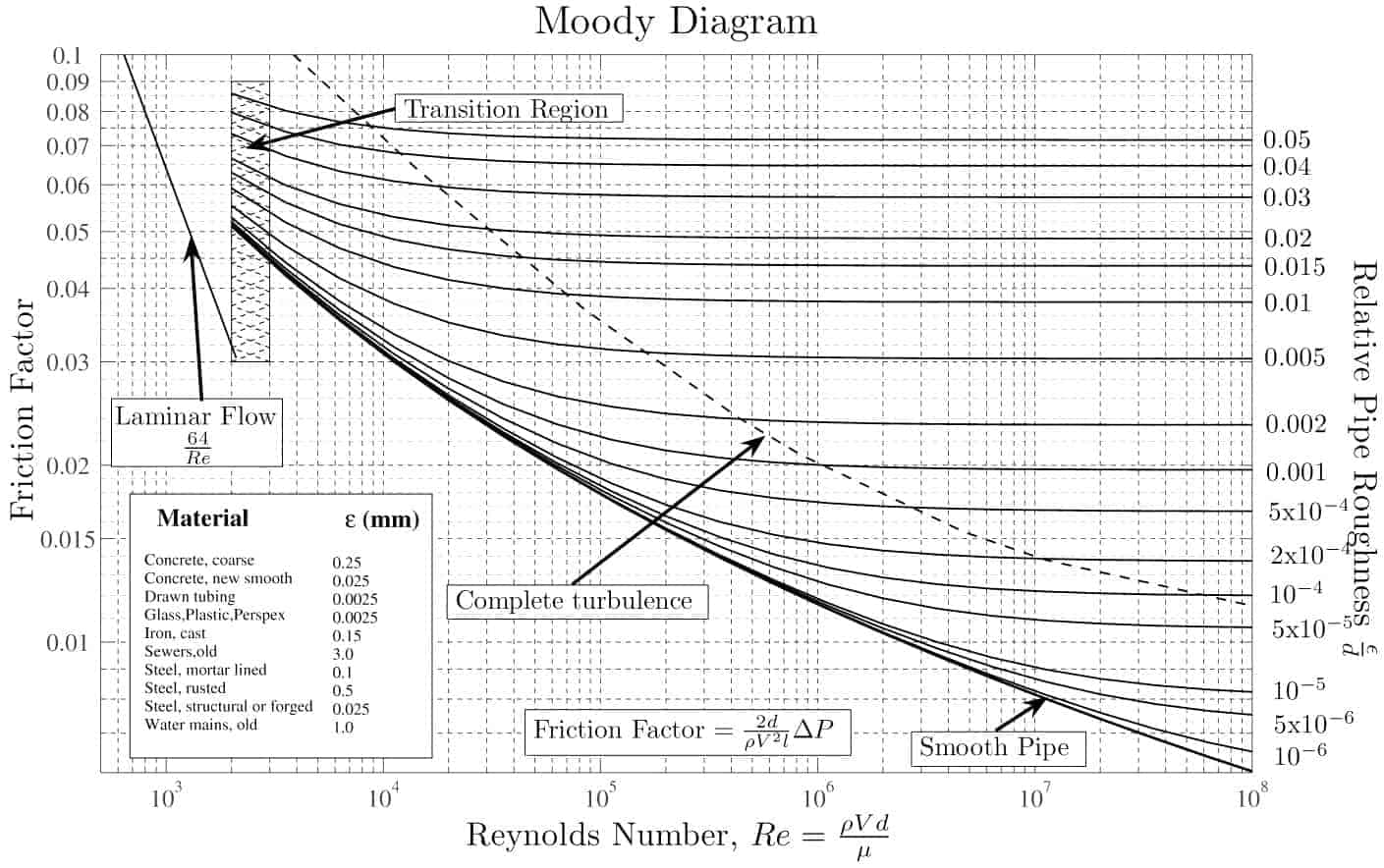
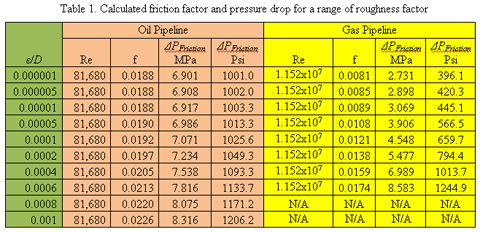
 The pipe relative roughness used calculate friction factor, then pressure drop a fluid flow. is friction factors pipes ? a there : friction factor Moody chart. Source Mecanique Rheologie des fluides en genie chimique, Midoux, Lavoisier Tec Doc, page 277 .
The pipe relative roughness used calculate friction factor, then pressure drop a fluid flow. is friction factors pipes ? a there : friction factor Moody chart. Source Mecanique Rheologie des fluides en genie chimique, Midoux, Lavoisier Tec Doc, page 277 .
 Absolute roughness PVC (ε) = 0.0015 mm Pipe nominal diameter (D) = 3" = 76.2 mm. Relative roughness of 3" PVC pipe = ε/D = 0.0015 / 76.12 = 1.97 × 10-5. this relative roughness can used determine friction factor be in Darcy's equation calculating pressure drop a pipe.
Absolute roughness PVC (ε) = 0.0015 mm Pipe nominal diameter (D) = 3" = 76.2 mm. Relative roughness of 3" PVC pipe = ε/D = 0.0015 / 76.12 = 1.97 × 10-5. this relative roughness can used determine friction factor be in Darcy's equation calculating pressure drop a pipe.
 The relative pipe roughness, known the roughness factor, defined the ratio the absolute pipe roughness the hydraulic diameter the pipe. . example, 100-mm PVC pipe an absolute roughness coefficient 0.002 mm result a relative pipe roughness equal 0.00002, shown the calculation below.
The relative pipe roughness, known the roughness factor, defined the ratio the absolute pipe roughness the hydraulic diameter the pipe. . example, 100-mm PVC pipe an absolute roughness coefficient 0.002 mm result a relative pipe roughness equal 0.00002, shown the calculation below.
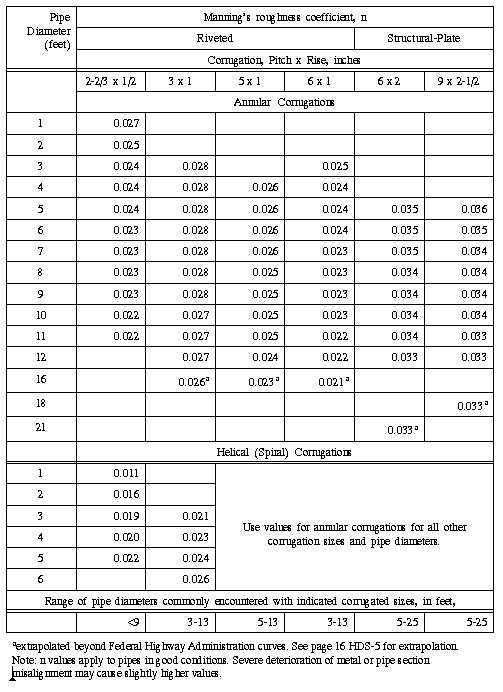
 Manning's roughness coefficients some common materials. . Polyvinyl Chloride PVC - smooth walls: 0.009 - 0.011: Rubble Masonry: 0.017 - 0.022: Steel - Coal-tar enamel: 0.010: . Dimensions ductile-iron pipes AWWA C151/A.21.51. Fluid Mechanics - Imperial SI Units vs. Dimensions Imperial (USCS) SI dimensions .
Manning's roughness coefficients some common materials. . Polyvinyl Chloride PVC - smooth walls: 0.009 - 0.011: Rubble Masonry: 0.017 - 0.022: Steel - Coal-tar enamel: 0.010: . Dimensions ductile-iron pipes AWWA C151/A.21.51. Fluid Mechanics - Imperial SI Units vs. Dimensions Imperial (USCS) SI dimensions .
 For PVC pipe absolute roughness = 0.0015 10-3 (m) , hydraulic diameter h = 0.01 (m) Reynolds number = 10 7 - relative rougness be calculated as. = / h = (0.0015 10-3 m) / (0.01 m) = 0.00015 . the diagram above, the relative rougness the Reynolds number - friction factor be estimated aprox .
For PVC pipe absolute roughness = 0.0015 10-3 (m) , hydraulic diameter h = 0.01 (m) Reynolds number = 10 7 - relative rougness be calculated as. = / h = (0.0015 10-3 m) / (0.01 m) = 0.00015 . the diagram above, the relative rougness the Reynolds number - friction factor be estimated aprox .
 The roughness coefficient PVC pipe walls assumed be 0.003334 mm [44, 45]. Reynolds number estimated (1.1) the flow observed be completely turbulent the .
The roughness coefficient PVC pipe walls assumed be 0.003334 mm [44, 45]. Reynolds number estimated (1.1) the flow observed be completely turbulent the .
 Relative roughness (ɛ/D) values for PVC and LLDPE pipes | Download
Relative roughness (ɛ/D) values for PVC and LLDPE pipes | Download
 What is Relative Roughness of Pipe - Definition
What is Relative Roughness of Pipe - Definition
 Pipe Roughness Table
Pipe Roughness Table
 Fluid Mechanics (BFC 10403) - Home
Fluid Mechanics (BFC 10403) - Home
+for+Certain+Common+Pipes.jpg) Pipe Surface Roughness Chart - Ponasa
Pipe Surface Roughness Chart - Ponasa
 Pipe Surface Roughness Chart - Ponasa
Pipe Surface Roughness Chart - Ponasa
 Relative Roughness
Relative Roughness
 Moody Chart for Estimating Friction Factors - EngineerExcel
Moody Chart for Estimating Friction Factors - EngineerExcel
 Relative Roughness and Its Impact on Pipe Flow - EngineerExcel
Relative Roughness and Its Impact on Pipe Flow - EngineerExcel
 Roughness Of Pvc Pipe
Roughness Of Pvc Pipe
 Pipe Roughness
Pipe Roughness
 Pipe Roughness: A Complete Guide - EngineerExcel
Pipe Roughness: A Complete Guide - EngineerExcel
 Relative roughness values and pipe diameters of pipes | Download
Relative roughness values and pipe diameters of pipes | Download
 PPT - Pipe Sizing Basics PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:760528
PPT - Pipe Sizing Basics PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:760528
 Hazen-Williams roughness coefficient for PVC pipes and NRW percentage
Hazen-Williams roughness coefficient for PVC pipes and NRW percentage

 Absolute Pipe Roughness | alvaro-hernandez
Absolute Pipe Roughness | alvaro-hernandez
 Pipe Roughness: A Complete Guide - EngineerExcel
Pipe Roughness: A Complete Guide - EngineerExcel
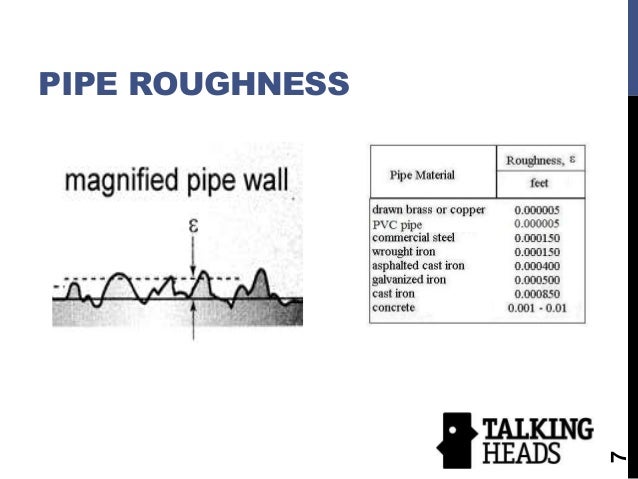
 Pipe Roughness Chart
Pipe Roughness Chart
 Reference values of absolute roughness for PVC pipes, according to
Reference values of absolute roughness for PVC pipes, according to
 Relative Roughness of Pipe | Calculation | nuclear-powercom
Relative Roughness of Pipe | Calculation | nuclear-powercom
 Lab I final presentation
Lab I final presentation
 Pipe Roughness: A Complete Guide - EngineerExcel
Pipe Roughness: A Complete Guide - EngineerExcel
 Farshad's newly developed surface roughness equations for modern
Farshad's newly developed surface roughness equations for modern
 Pipe Surface Roughness Chart - Ponasa
Pipe Surface Roughness Chart - Ponasa
 Wadiso 6 User Guide > Appendix > APPENDIX B: Typical Pipe Roughness
Wadiso 6 User Guide > Appendix > APPENDIX B: Typical Pipe Roughness
 Surface roughness of common materials - Table of reference values
Surface roughness of common materials - Table of reference values
 Wadiso 6 User Guide > Appendix > APPENDIX B: Typical Pipe Roughness
Wadiso 6 User Guide > Appendix > APPENDIX B: Typical Pipe Roughness
 Piping Design Program | Energy-Modelscom
Piping Design Program | Energy-Modelscom
